Jakarta - Indonesian, begins with fever and rash in the mouth the appearance of red spots, which later became a lesion or blister. When you see these symptoms, be careful! Singapore could be a flu or HFMD (hand, foot and mouth disease).
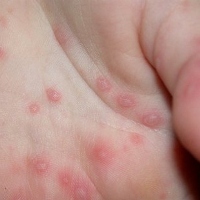
Initial symptoms are fever for 2 days and a mouth full of sores. On the child's hands and feet appear red spots. Moreover, he did not want to eat, but still want to drink milk.
It 'true that this disease can be dangerous? There are rumors, as dangerous as avian flu affect Singapore? My child needs to be treated? When the children to the disease, not panic. HFMD is usually mild viral infection, provided that immediately gets the right treatment.
Causes and symptoms of HFMD
HFMD recently rampant again. Later, the case is quite commonly found in Indonesia. The flu is actually a term for HFMD in Singapore this is less precise. This term appears for the outbreak of HFMD in Singapore in 2000, so the disease is more commonly known as influenza Singapore.
Virus derived from the group of enteroviruses (non-polio) is a cause of HFMD. In it are Coxsackie group type A (A1-A24), Coxsackie type B (B1-B26), Echovirus (groups 1-33), and enteroviruses (68-71). The most common cause in the case of outpatient care is Coxsackie A16. While enterovirus infection that requires treatment usually leads to enterovirus 71.
HFMD symptoms of fever was initiated for 2-3 days, followed by sore throat (pharyngitis), no appetite, runny nose, which is a flu-like symptoms are generally not lethal. Then, derived vesicles (fluid-filled bumps) on the mouth, then broke, wounds or blisters in the mouth such as sores on the tongue, gums, cheeks, that we feel the pain difficult to digest.
This is not itchy rashes on the palms of the hands and feet. Sometimes rashes in the buttocks. Although his name hand, foot and mouth, the rash does not appear in all three sites. Sometimes just in the mouth and hand. In general, this eruption is better by itself and did not need hospital treatment.
HFMD transmission and management
In general, HFMD is not dangerous. Coxsackie A16 HFMD is a mild disease and heal in 7-10 days. Complications are rare. Very rare to find children with Coxsackie virus infection in viral meningitis with symptoms of high fever, headache, stiff neck, which requires hospitalization.
Group of enteroviruses obtained from HFMD Enterovirus 71 can cause viral meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain), encephalitis (brain inflammation), or paralysis (paralysis). Due to enterovirus 71 encephalitis can be fatal.
The disease is highly contagious and often occur in summer. Transmission through the digestive tract, respiratory tract, ie from wheat saliva, nasal mucus, saliva, faeces, liquids from the wound, and other body fluids.
Indirect contact transmission can occur through the goods, towels, clothes, food equipment and toys are contaminated with secretions (fluids) of the body. Since the starting infected until symptoms begin to appear (incubation period) is 3-7 days. Fever is the first symptom of HFMD. A will transmit the disease within the first week when she is sick.
HFMD most often affects children under the age of 10 years. Every person, whether child or adult, has the risk of contracting the infection, but not everyone infected will hurt. Infants, children and adolescents are more vulnerable to infection and disease, HFMD is because their immune antibodies and weaker than adults.
HFMD was diagnosed by the history of the disease courseand physical examination. While the laboratory diagnosis for the detection of the virus can be done by taking samples of stool, rectal swabs or swabs serobrospinal fluid, wound swabs or swabs in the mouth, throat, skin vesicles, and brain biopsy.
There is no specific treatment for enterovirus infections. Ensure adequate rest and symptomatic treatment to relieve symptoms of fever and pain in the mouth. Children can be given an antiseptic for the mouth area, analgesic-antipyretic such as paracetamol, plenty of fluids and other supportive treatments. When symptoms are severe enough, the patient should be hospitalized.
The symptoms are severe enough, among others, fever, fever that is high (temperature> 39 ° C), fever does not go down and down, tachycardia (pulse becomes faster), takipneu (shortness of breath becomes quick and), lazy eating, vomiting, diarrhea, repeated dehydration, fatigue and drowsiness continues, pain in the neck, arms and legs, or paralysis of the cranial nerve.
To prevent HFMD with hygiene, environmental sanitation and personal. The easiest way is to get used to always wash your hands, especially when near the patient.
The disinfection of equipment needed food, toys, and towels that may have been contaminated with liquid chlorine. Avoid contact with HFMD patient and rest while children with HFMD from school or childcare, to prevent transmission of the virus to other children.
Nursing Tips HFMD
1. Immediate medical attention to determine if the child or the patient is exposed to HFMD
2. Isolate the patient
3. Keep
4. Encourage adequate rest
5. Provide adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration
6. Provide proper nutrition and balanced diet
7. Give symptomatic medications to reduce symptoms of fever and sore mouth
8. The patient not to go (to school or office) for 7-10 days after the rash appears
AuthorDr. U. Rasma Ginting, Sp. ATeam Child Specialist Doctors Eka Hospital BSD Tangerang - Indonesian
Initial symptoms are fever for 2 days and a mouth full of sores. On the child's hands and feet appear red spots. Moreover, he did not want to eat, but still want to drink milk.
It 'true that this disease can be dangerous? There are rumors, as dangerous as avian flu affect Singapore? My child needs to be treated? When the children to the disease, not panic. HFMD is usually mild viral infection, provided that immediately gets the right treatment.
Causes and symptoms of HFMD
HFMD recently rampant again. Later, the case is quite commonly found in Indonesia. The flu is actually a term for HFMD in Singapore this is less precise. This term appears for the outbreak of HFMD in Singapore in 2000, so the disease is more commonly known as influenza Singapore.
Virus derived from the group of enteroviruses (non-polio) is a cause of HFMD. In it are Coxsackie group type A (A1-A24), Coxsackie type B (B1-B26), Echovirus (groups 1-33), and enteroviruses (68-71). The most common cause in the case of outpatient care is Coxsackie A16. While enterovirus infection that requires treatment usually leads to enterovirus 71.
HFMD symptoms of fever was initiated for 2-3 days, followed by sore throat (pharyngitis), no appetite, runny nose, which is a flu-like symptoms are generally not lethal. Then, derived vesicles (fluid-filled bumps) on the mouth, then broke, wounds or blisters in the mouth such as sores on the tongue, gums, cheeks, that we feel the pain difficult to digest.
This is not itchy rashes on the palms of the hands and feet. Sometimes rashes in the buttocks. Although his name hand, foot and mouth, the rash does not appear in all three sites. Sometimes just in the mouth and hand. In general, this eruption is better by itself and did not need hospital treatment.
HFMD transmission and management
In general, HFMD is not dangerous. Coxsackie A16 HFMD is a mild disease and heal in 7-10 days. Complications are rare. Very rare to find children with Coxsackie virus infection in viral meningitis with symptoms of high fever, headache, stiff neck, which requires hospitalization.
Group of enteroviruses obtained from HFMD Enterovirus 71 can cause viral meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain), encephalitis (brain inflammation), or paralysis (paralysis). Due to enterovirus 71 encephalitis can be fatal.
The disease is highly contagious and often occur in summer. Transmission through the digestive tract, respiratory tract, ie from wheat saliva, nasal mucus, saliva, faeces, liquids from the wound, and other body fluids.
Indirect contact transmission can occur through the goods, towels, clothes, food equipment and toys are contaminated with secretions (fluids) of the body. Since the starting infected until symptoms begin to appear (incubation period) is 3-7 days. Fever is the first symptom of HFMD. A will transmit the disease within the first week when she is sick.
HFMD most often affects children under the age of 10 years. Every person, whether child or adult, has the risk of contracting the infection, but not everyone infected will hurt. Infants, children and adolescents are more vulnerable to infection and disease, HFMD is because their immune antibodies and weaker than adults.
HFMD was diagnosed by the history of the disease courseand physical examination. While the laboratory diagnosis for the detection of the virus can be done by taking samples of stool, rectal swabs or swabs serobrospinal fluid, wound swabs or swabs in the mouth, throat, skin vesicles, and brain biopsy.
There is no specific treatment for enterovirus infections. Ensure adequate rest and symptomatic treatment to relieve symptoms of fever and pain in the mouth. Children can be given an antiseptic for the mouth area, analgesic-antipyretic such as paracetamol, plenty of fluids and other supportive treatments. When symptoms are severe enough, the patient should be hospitalized.
The symptoms are severe enough, among others, fever, fever that is high (temperature> 39 ° C), fever does not go down and down, tachycardia (pulse becomes faster), takipneu (shortness of breath becomes quick and), lazy eating, vomiting, diarrhea, repeated dehydration, fatigue and drowsiness continues, pain in the neck, arms and legs, or paralysis of the cranial nerve.
To prevent HFMD with hygiene, environmental sanitation and personal. The easiest way is to get used to always wash your hands, especially when near the patient.
The disinfection of equipment needed food, toys, and towels that may have been contaminated with liquid chlorine. Avoid contact with HFMD patient and rest while children with HFMD from school or childcare, to prevent transmission of the virus to other children.
Nursing Tips HFMD
1. Immediate medical attention to determine if the child or the patient is exposed to HFMD
2. Isolate the patient
3. Keep
4. Encourage adequate rest
5. Provide adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration
6. Provide proper nutrition and balanced diet
7. Give symptomatic medications to reduce symptoms of fever and sore mouth
8. The patient not to go (to school or office) for 7-10 days after the rash appears
AuthorDr. U. Rasma Ginting, Sp. ATeam Child Specialist Doctors Eka Hospital BSD Tangerang - Indonesian


0 comments:
Post a Comment